How to stop gag reflex from anxiety is a common question. Many people face this issue but feel too shy to discuss it. When you feel anxious, your body reacts fast. One clear sign is a sudden gagging or choking feeling. This happens because stress can trigger your vagus nerve. It also makes your throat muscles tighten.
These changes can set off your gag reflex. Some people gag in the morning. Others feel it while brushing their teeth or speaking in public. It can feel scary, but it is not usually dangerous. Understanding why this happens can help you feel more secure. In this guide, we will explain the link between anxiety and gagging, list key symptoms, and share simple ways to calm your body and stop the reflex.
What Is the Gag Reflex?
The gag reflex is your body’s natural defense system. It stops food or other objects from entering your airway. Most people don’t notice it until it becomes too sensitive or gets triggered by anxiety.
How the Gag Reflex Works
The reflex starts when something touches the soft palate or the back of your throat. This can be anything from food to a toothbrush or even a pungent smell. The vagus nerve quickly sends a signal to your brainstem. Your brain responds by tightening the muscles in your throat. You gag or cough to clear the threat. This happens fast and automatically.
Why This Reflex Matters
The gag reflex protects you from choking. It’s a regular part of how your body keeps the airway clear. Some people have an overly sensitive gag reflex. Even a light touch or stress can trigger it. For others, anxiety alone can set it off. When you feel tense, your throat may tighten. You may experience a lump in the throat, also known as globus sensation. Even without anything in the throat, the reflex can still activate.
The Mind-Body Link
When anxiety rises, your body reacts as if danger is near. This can overstimulate the gag reflex. It’s why some people gag in the morning or while brushing their teeth. Understanding how this reflex works makes it easier to manage both the physical response and the underlying anxiety.
How Anxiety Triggers the Gag Reflex
Many people are surprised when anxiety causes gagging. It might happen at home, in the morning, or even during public speaking. The body and mind are deeply linked. When stress levels rise, they can trigger a chain reaction that culminates in a tight throat and a sudden gag reflex.
The Stress Response
When you feel anxious, your body goes into “alert” mode. This is called the stress response. Your brain releases stress hormones. Your heart beats faster, and your breathing becomes more rapid. At the same time, the vagus nerve becomes more active. This nerve connects your brain to your throat, stomach, and other organs. When it is overstimulated, your throat muscles tighten. This can trigger the gag reflex even without a physical object being present.
Throat Tightness and Globus Sensation
A common sign of anxiety is a lump in the throat, also known as globus sensation. It feels like something is stuck, but nothing is there. This feeling often appears during panic, high stress, or early in the day. It can make you swallow more often, which sometimes makes gagging worse.
Situations That Make It Stronger
Certain moments can make the reflex more sensitive. Examples include brushing your teeth, eating in public, or feeling nervous before a big event. Morning gagging is also common when anxiety levels are high after waking up. These triggers don’t mean anything is wrong with your throat. They show how anxiety and the gag reflex are linked.
Why Understanding This Helps
Once you know how anxiety triggers gagging, the symptom feels less frightening. You start to see it as a body reaction, not a sign of danger. This shift is the first step toward calming the gag reflex and easing the physical signs of anxiety.
Common Symptoms That Accompany Anxiety: Gag Reflex
When the gag reflex is triggered by anxiety, it rarely comes alone. Many people notice other physical signs that make the experience uncomfortable. Recognizing these symptoms helps you understand your body and manage the reflex more effectively. Signs to Watch For:
- Nausea: A feeling of wanting to vomit often appears alongside gagging.
- Dry heaving: You might make gagging motions without anything coming up.
- Throat tightness: The throat muscles feel tense or constricted.
- Lump in the throat (Globus sensation): A false sense of something stuck in your throat.
- Shortness of breath: Anxiety can make breathing feel more difficult, exacerbating the gag reflex.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: The stress response can affect your balance.
- Swallowing difficulties: Feeling the urge to swallow often without relief.
Why These Symptoms Happen
All these symptoms happen because anxiety activates your stress response system. Your vagus nerve and throat muscles react quickly. Even small triggers, such as brushing your teeth or thinking about food, can activate the hyperactive gag reflex.
Recognizing these signs early helps you act quickly. Simple strategies, such as deep breathing, relaxing the throat muscles, or practicing grounding exercises, can help reduce discomfort and prevent the gag reflex from escalating.
How to Stop Gag Reflex from Anxiety: Immediate Techniques
The gag reflex triggered by anxiety can feel sudden and overwhelming. Many people want fast relief when it happens. The good news is that there are simple, effective ways to calm your throat muscles, control your vagus nerve, and reduce the reflex immediately. These techniques are safe and easy to use, making them suitable for use in any setting.

1. Deep Breathing to Calm the Body
Deep breathing is one of the fastest ways to reduce anxiety. Try slow nasal breaths. Inhale for four counts, hold for two, then exhale for six. This signals your body to relax. It lowers stress hormones and calms the vagus nerve, making gagging less likely. Even a few breaths can help you regain control.
2. Grounding Exercises for Focus
Distraction can help stop the reflex. A simple 5-4-3-2-1 technique works well. Notice five things you see, four things you touch, three things you hear, two things you smell, and one thing you taste. This shifts attention away from the hyperactive gag reflex and the anxiety behind it.
3. Relax Your Throat Muscles
Tension in the throat muscles can trigger a gag reflex. Try gently stretching your neck and moving your jaw. Swallow slowly and sip cold water to relax your soft palate. Humming lightly also helps calm the throat reflex.
4. Use Simple Physical Tricks
Pressing the tongue gently against the roof of the mouth or touching the back of your teeth can help override the reflex. Even chewing gum or lightly sipping water can distract the body from the gag reflex.
5. Stay Mindful of Anxiety Triggers
Notice when anxiety causes your gag reflex. Is it morning, brushing teeth, or public speaking? Awareness allows you to act quickly using these techniques before gagging escalates.
Consistently using these steps can make the gag reflex feel less frightening. You begin to see it as a normal body reaction rather than a threat. Over time, you gain control over anxiety and the reflex, feeling calmer and more confident in daily life.
Long-Term Strategies to Reduce Anxiety Gag Reflex
While immediate techniques help in the moment, long-term strategies make the gag reflex from anxiety easier to manage over time. These methods focus on reducing overall anxiety, calming the body, and gradually decreasing sensitivity in the throat muscles and vagus nerve.
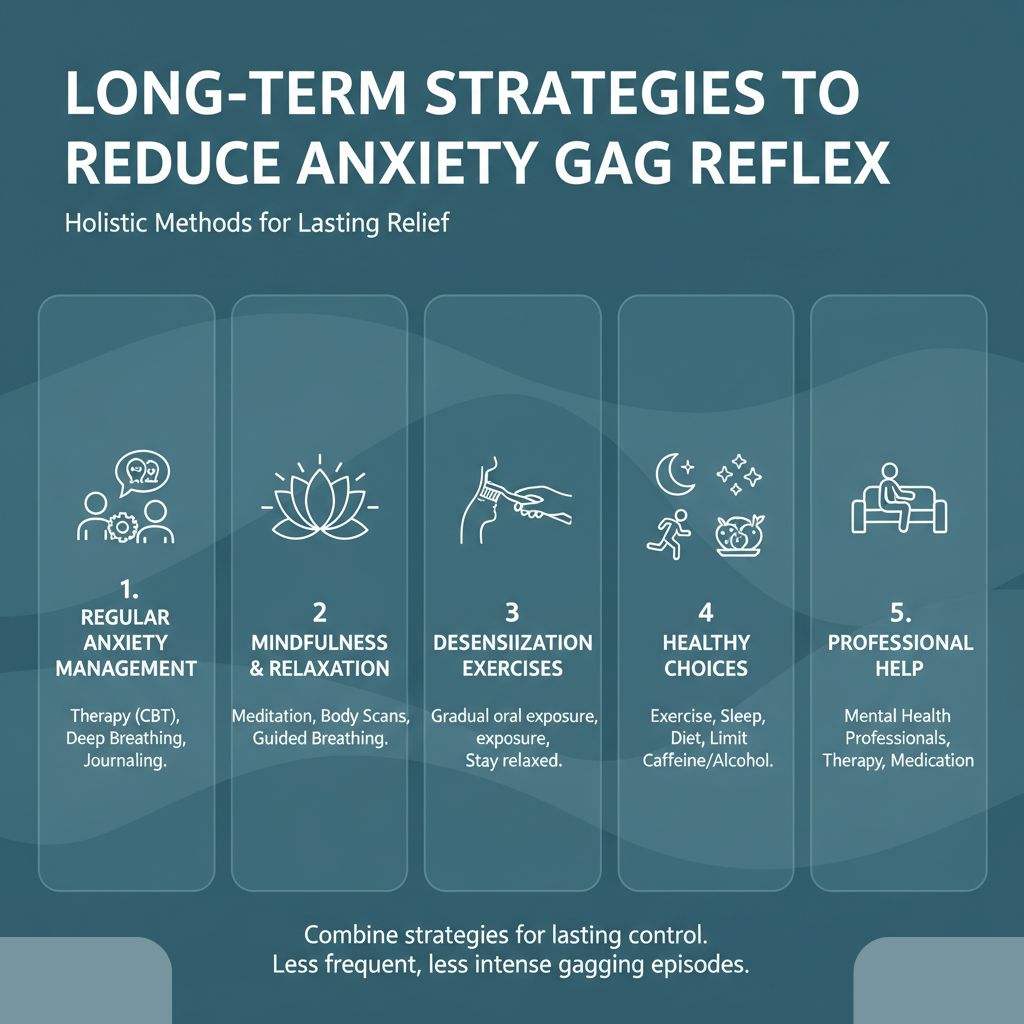
1. Regular Anxiety Management
Therapy, especially Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), can help you understand triggers and change thought patterns. Practicing daily stress management techniques like deep breathing or journaling keeps anxiety from building up. Over time, this reduces episodes of anxiety and gag reflex.
2. Mindfulness and Relaxation Training
Mindfulness teaches you to stay in the present moment. Simple exercises, such as meditation, body scans, or guided breathing, help relax the throat muscles and calm the vagus nerve. Even 10–15 minutes a day can lower the chance of reflex activation.
3. Desensitization Exercises
Gradual exposure can reduce the reflex over time. Start by lightly touching the back of your throat with a toothbrush or tongue depressor while staying relaxed. Increase exposure slowly. This trains your body to respond less strongly, helping with a hyperactive gag reflex triggered by anxiety.
4. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and a balanced diet all help your body manage stress effectively. Avoiding excessive caffeine or alcohol can also reduce anxiety symptoms that trigger gagging.
5. Professional Help When Needed
If the reflex persists or disrupts daily life, consulting a mental health professional or a psychiatrist is wise. They can recommend therapy, coping strategies, or, if necessary, short-term treatment to reduce extreme anxiety reactions.
By combining these long-term strategies with immediate techniques, you can gain lasting control over the gag reflex. Over time, anxiety becomes easier to manage, and episodes of gagging become less frequent and less intense.
When to See a Professional
Most cases of gag reflex caused by anxiety are harmless and manageable at home. However, there are times when professional help is necessary. Knowing when to seek guidance can prevent stress from escalating and provide targeted support.
Signs You Should Get Help
- Persistent gagging: If it happens every day or during many routine activities.
- Severe anxiety: When anxiety feels overwhelming or affects daily life.
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing: Even mild trouble should be evaluated.
- Interference with eating or speaking: The reflex disrupts everyday eating and speaking routines.
- No improvement with self-help techniques: Immediate and long-term strategies don’t reduce episodes.
Types of Professional Support
A mental health professional or psychiatrist can assess whether anxiety is the primary trigger. They can recommend therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), relaxation training, or mindfulness practices. In rare cases, medical tests may be suggested to rule out throat or digestive issues.
Why Seeking Help Matters
Getting professional help doesn’t mean there is something “wrong” with you. It simply provides guidance and tools to manage both anxiety and the gag reflex more effectively. Early support can reduce fear, improve daily function, and prevent the reflex from worsening.
At Peniel Psychiatry, our trained experts can evaluate your symptoms and create a personalized plan tailored to your specific needs. This ensures both your physical and mental well-being are addressed. Schedule Your Intake Appointment to get a customized care plan and start your journey toward lasting wellness.
Final Thoughts
The gag reflex from anxiety can feel uncomfortable and even frightening. But it is a normal body response, and it can be managed. Understanding how anxiety triggers gagging, recognizing symptoms, and using both immediate techniques and long-term strategies can make a big difference.
You are not alone. Many people experience a hyperactive gag reflex caused by stress, and simple actions can provide relief. Practices such as deep breathing, grounding exercises, and throat relaxation can help in the moment. Over time, mindfulness, CBT, and gradual desensitization reduce sensitivity and build confidence.
Take the Next Step
If anxiety or gag reflexes interfere with your daily life, seeking professional support can help. At Peniel Psychiatry, trained experts provide personalized strategies to manage both anxiety and the physical reflexes that come with it. Early guidance can reduce discomfort, restore confidence, and improve daily functioning.
Don’t wait. Take control of your anxiety gag reflex today and feel calmer, safer, and more confident in your daily life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can anxiety really cause gagging?
Yes. Anxiety can trigger your vagus nerve and tighten throat muscles, causing a sudden gag reflex. Even without a physical object, the body reacts as if there is a threat. This is a normal response and usually harmless, though it can be uncomfortable.
How long does the anxiety gag reflex last?
The duration varies. For most people, episodes last a few minutes until the body relaxes. Using deep breathing, grounding exercises, or throat relaxation can quickly stop the reflex. Over time, mindfulness and therapy can reduce the frequency of these episodes.
Is gagging from anxiety dangerous?
Generally, it is not dangerous. The gag reflex is a protective response. However, if it interferes with breathing, eating, or daily life, it is essential to seek professional help. Understanding the reflex and managing anxiety symptoms reduces discomfort.
Can medication help with anxiety and the gag reflex?
In some cases, medication may help control anxiety symptoms that trigger gagging. However, doctors usually combine this with therapy, relaxation techniques, and lifestyle changes. Professional guidance ensures safe and effective treatment.
What if gagging happens every morning?
Morning gagging often occurs when anxiety levels are higher upon waking. Simple steps, such as slow breathing, sipping water, or gentle stretching, can help. Practicing long-term strategies, such as mindfulness or CBT, can reduce sensitivity and prevent daily episodes.
How can I stop a gag reflex naturally?
Natural methods include deep breathing, tongue pressing, throat relaxation exercises, and gradual desensitization. Consistent practice, combined with anxiety management, reduces reflex sensitivity and builds confidence in daily activities.




